CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:
Unit 2 - Challenges in the human Environment
The Changing Economic World

CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW: CW Date: February 2018
Title:
The Development Gap - Introduction
See Slide Show HERE (covers the next two sessions and activities)
Source sheet - HERE (Print out)
Entry Task:
a. Comment on the development of the country that this family live in.
b. What do we mean by the term "Development".
Key Terms:
Development - Positive change that makes things better.
GNI - Gross National Income
HDI - Human Development Index
Quality of Life - standard of health, comfort, and happiness experienced by an individual or group
Standard of Living - the degree of wealth and material comfort available to a person or community.
Notes:
What do we mean by development?
The world is unequal in many ways... including economic development and people's quality of life. The "Development Gap" refers, then to the differences in the Standard of Living between the richest and poorest countries.
As places develop, people's standard of living and their quality of life usually improve.
Development is influenced by a number of factors:
1. Environmental factors - eg exposure to natural hazards
2. Economic factors - include trade and debt
3. Social factors - such as access to clean water and education
4. Political factors - eg stability of government or civil war
How is development measured?
a. Economic measures - For example GNI = the total value of goods and services produced by a country plus money earned from and paid to other countries (it is expressed as a per capita amount).
GNI is used by the World Bank to categorise countries into:
- High,
- Upper middle,
- Lower Middle, and
- Low
income groups. UK et al would be High Income Countries (HICs) and most countries in Africa are low Income Countries (LICs).
As an average, however, it obscures internal variations. For example, a country with a low population and high GNI might have a low Standard of Living because the wealth of the country in held my a minority of the population. Conversely, in a LIC, there will be groups who have a high standard of living.
Note: some countries that have begun a process of rapid economic development and industrialisation are termed NEEs (Newly Emerging Economies) eg Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (the so-called BRICS)... or MINT countries (Malaysia, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey).

CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:CW Date: February 2019
See slide show (above) and Activities Hand Out (Above)
Title:
The Development Gap - Continued
Entry Task:
Give an example of an environmental factor that can influence a countries development... explain how.
Name a place that you have studied where development is impeded by environmental factors.
Activity:
Complete question 1 and 2 from the hand out provided.
Look at the image below again... what are we able to deduce about this family's SoL?
What about their QoL?
Continuing notes:
b. Composite Measures of Development- In addition to economic measures, some methods try to combine social indicators with economic measures. The Human Development Index is one measure that does this to produce an "index" between 0 and 1. It aims to show how people are benefiting from a countries economic growth.
The index uses the following data:
- Life expectancy
- Number of years in education
- GNI per capita
Countries can be ranked using HDI - in 2014, Norway was top of the list with an HDI of 0.944 (UK was 14th with 0.930) and Nigeria was bottom (188th) with an HDI of 0.348. The lowest ten countries in the ranking are all in Africa.
Activity:
Complete question 3 on the hand out.
c. Quality of Life - Economic and social measures give a broad indication of development, but they do not measure an individual's Quality of Life.
However, QoL is difficult to quantify since it means different things to different people at different times... safety and security might be high on the agenda of refugees from Syria, whereas gender equality, voting rights and happiness might be more important to people living in other places.
Activity:
1. Complete question 4 and 5 from the hand out ( HERE).
Topological Maps... is this one?

A topological map is a type of diagram in which:
- Only vital information remains and unnecessary detail has been removed.
- Scale is lacking, and distance and direction are subject to change and variation
- Relationship between points is maintained.
Q. how does the map (Q 5) on your Hand Out conform to this definition?
2. Read pp 196 of the text.
3. Complete questions 6 and 7 from the Hand out.
NL: limitations of econ and soc measures... correlation... pp197

CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:
CW Date: 26th February 2019
Lesson Covered as Interviewing... see HERE
See resource sheet - HERE
Title:
What are the limitations of economic and social measures of development?
Entry Task:
Social or economic indicator?
- GNI
- Death Rate
- Doctors per thousand people
- Birth Rate
Does a high value for these measures suggest high or low development?
Key Terms:
Economic indicators -
Social indicators -
Correlation -
The use of a single indicator of development can be misleading... why?
The GNI in this oil producing country is high...

Saudi Arabia
55,760 PPP dollars

This person (right) also comes from Saudi Arabia and is more representative of the general population.
Notes:
A single indicator may be misleading and unrepresentative of the whole country. The GNI per capita of Saudi Arabia is an average, but because a great deal of the countries wealth is in the possession of relatively few people it creates an unrealistic view of the countries economic wealth.
Other factors that could cause indicators to be misleading:
- Data out of date.
- Data may be missing due to difficulty of collection.
- Data provided is inaccurate and unreliable due to government corruption or problems in the process of data collection.
- Data may not take into account subsistence production or earnings in the "informal economy".
In some countries over 80% of the countries wealth may be held by just 10% of the population. Wealth may also be much greater in cities while the rural surroundings are poor and undeveloped (hence the high levels of rural to urban migration in many LICs).
Activities:
1. Complete the "Maths skills" task on pp 197 (HDI plus one other variable only).
2. Using the table on pp 196, identify the development data that appears to be anomalous for Turkey. (BIRTH RATE) - Suggest why.
3.
CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:
CW Date:
Title:
Development and the Demographic Transition.
DTM Source Sheet - HERE
Entry Task:
Look at the terms below which make up part of our title... what do each of them, individually mean?
Can you work out, then what the Demographic Transition Model is?
Key Terms:
Demographic - Relating to the structure of a population i.e. birth and death rates.
Transition - Change
Model - A simplified version of the reality.
The graph below, and provided, shows how birth and death rates change (transition) over time and as countries become increasingly developed.
DTM on Slide for annotation (alternative - Describe the changes and reasons - as tasks below) - HERE

18th Century:
The death rate for infants was super high in these ages because of their unhygienic practices. The average age was thirty five while fifty was considered a ripe old age.

Life in the 20th Century... HERE
Activity:
(Alternatively annotate onto the Slide - Link above)
describe the following for each Stage of the Model:
- Birth Rate
- Death Rate
- Total Population
- Natural population change (the difference between BR and DR)
e.g.
Stage 1:
Birth rate and death rate are both high which keeps the total population low. Natural population change fluctuates between small natural increase and small natural decline.
2. Suggest reasons for the differences that you have described.
3. To what extent are the different features of the DTM from Stage 1 to Stage 5 the consequence of increasing development? Explain your answer giving examples from the model and referring to the examples on page 199 of the core text.
Above and below combined using the Slide Pres. (above and HERE)
CW Date: 5th March 2019
Title:
Development and the Demographic Transition.
1. Draw a sketch to illustrate the DTM. Add annotations to explain the economic changes that have led to changes as the model progresses through each Stage.
2. A falling Birth Rate is an indication that wealth is increasing... why is this?
3. An increasing Death Rate is a reflection of high levels of development. Suggest why.
4. Describe the population characteristics of countries in Stage 5 of the DTM. What negative effect might these characteristics have on a countries development and why?

PPPQ:

Home Work:
Due Date:

CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:CW Date: 8th March 2019
Title:
Demographic characteristics (population pyramids) and the Development Gap
Entry Task:
Key Terms:
Activities:
Complete activities 1 to 4 on pp 199 (work from last lesson.- Read pp 200/201 and complete activities 1 and 2 on pp201 (This will need to be completed for homework if not done in class)
Home Work:

CW Date: 8th March 2019
Title:
Population Characteristics and the DTM + Causes of differences in development.
Source: HERE
Entry Task:
Reading about Population Pyramids pp 200/201
Key Terms:
Economic - To do with wealth, finance and money.
Environmental - To do with aspects of the natural surroundings and systems.
Activities:
Population Characteristics:
Discuss and feedback (see worksheet/source -above):
a. What information is represented on a population Pyramid?
b. Make an outline sketch to show how Population Pyramids show these features?
See web page HERE
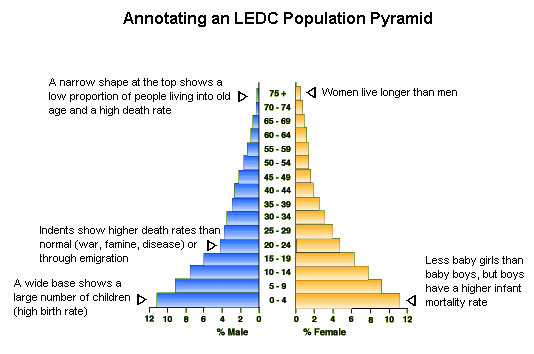
c. Contrast the shapes of the Population Pyramids of a Stage 1 and Stage 2 population.
d. To what extent does the Stage 5 Population Pyramid accurately reflect the DTM?

Challenge/Stretch:
Study the Population Pyramids on
pp 201. Use these to explain why Japan's population is both aging and declining.
Causes of a lack of development
pp 202/203
1. Outline the Historical, Economic and Environmental causes of a lack of development.
HW:
To what extent do you agree with the view that Economic factors are the most important causes of a lack of development?... approach this question by...
a. Reading the text pp 202/203
b. Discussing the question with a partner (try adopting opposing views).
c. Write a response (structure your answer as a for a 6 mark examination question)

CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:CW Date:
Title:
Population Pyramids and the DTM
Entry Task:
Key Terms:
Population Pyramid - A modified graph to show the age and gender structure of populations at a point in time.
DTM - Demographic Transition Model
Causes of a lack of develoment:
a. Economic - Factors linked to money eg Trade
b. Environmental/physical - Factors linked to the natural environment such as Natural Hazards.
c. Historical - Factors associated with past events and relationships between countries.
Activities: Source sheet: HERE
Home Learning: Kerboodle Skills Pod 16 + Test Worksheet: Here
-------------------------------------------------
Causes of uneven development (HERE) Extended answer style activities for remainder of the Development Gap unit (HERE)
CW DATE: 19th March 2019
TITLE:
How does uneven development cause migration?
ENTRY TASK:
Define the following key terms:
1. Migration
2. Immigration
3. EmigrationINTRODUCTION
Using examples (see pp 206) explain the differences between forced and voluntary migration.
What is meant by the terms Refugee; Displaced Person and Economic Migrant?
KEY TERMS:
See above
ACTIVITIES:
Having read through the text pp 205/6, answer the following questions:
1. What are the arguments for and against the UK taking in more economic migrants?
2. What are two reasons for the UK accepting refugees?
3. Summary:
Outline how uneven levels of development globally cause migration. Try to use specific examples of the source regions and host countries of migrants and consider the different types of migration covered above.PLENARY:
HW:
Suggest how European countries concerned about levels of migration should respond.
CW DATE: 19th and 22nd March 2019
TITLE:
How can the Development Gap be Reduced?
ENTRY TASK:
See HW task above.
INTRODUCTION
There are a range of strong moral, economic and security reasons for endeavoring to reduce inequalities between countries.
On the one hand, the lack of development in many countries means that people are living in appalling conditions... morally unacceptable. Furthermore, these conditions are, to a not inconsiderable extent, the result of historical exploitation by today's wealthy nations through, for example, political and economic colonialism. This exploitative process continues today, often perpetrated by large multinational corporations.
Economically, the success of nations depends on a market for goods and services. Richer countries are effectively bigger markets (irrespective of population) since they have greater purchasing power. As such, helping poor countries to grow economically provides existing wealthy nations with more places to sell their goods, services and know-how.
From a strategic point of view, conflict can be one outcome of a lack of hope of improvement... continuing poverty and a lack of development can drive people into violent responses. Conflict can also result from anger at being excluded from fair involvement in international development through, for example, international trade. It is also clear that low levels of education, a lack of equality and democracy in some countries leads to religious extremism, populations that are more easily persuaded to take up arms, greater levels of prejudice or racism and internal (as well as external) jealousies.
If there is a determination to live in a better, healthier and happier world, there must also be a commitment to reduce the disparities in quality of life and standards of living for all the World's inhabitants. While inequality remains, the World will continue to see large-scale movements of people from the poorer to richer areas, greater development gaps between countries, conflict, unstable economies and a continued ineffectiveness in dealing with such serious issues as climate change.KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
For this last section of the Development Unit
you have a choice of 20 mark essay titles (below):
A. Assess the relative merits of different approaches to reducing the development gap.
B. What strategies can be used to reduce disparities in development. Suggest which you consider to be most likely to succeed and explain why.
Alt. Diffn:
Describe three different approaches to reducing the development gap.
Why is there a development gap? Outline at least one way that the gap can be reduced.PLENARY:
HW:
Researching/drafting essay.
Writing up neatly.
CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.